Table of Contents
Cashpoint
Description
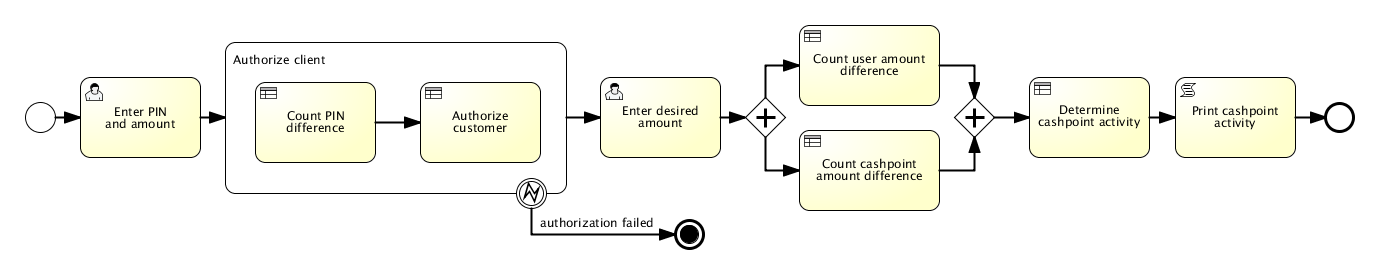
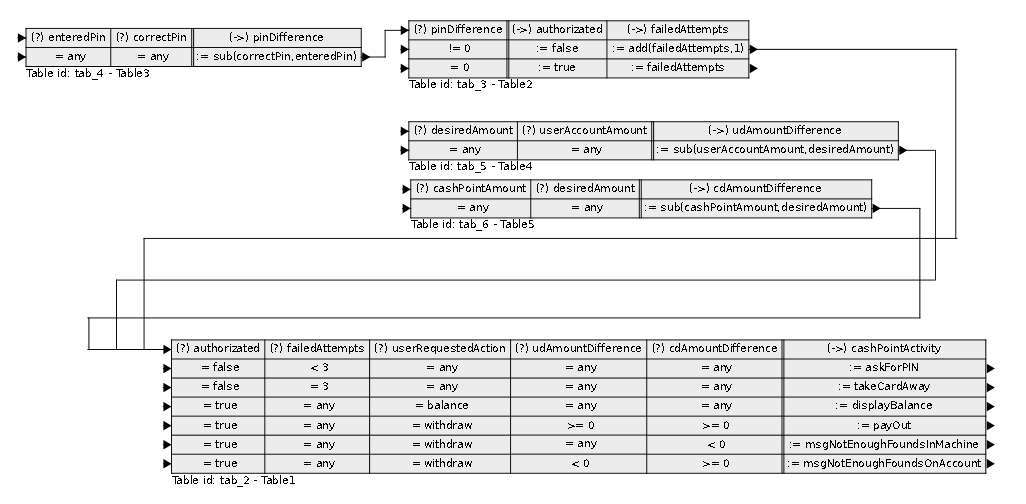
The system is composed of till which can access a central resource containing the detailed records of customers’ bank accounts. A till is used by inserting a card and typing in a Personal Identification Number (PIN) which is encoded by the till and compared with a code stored on the card. After successfully identifying themselves to the system, customers may either: make a cash withdrawal or ask for a balance of their account to be printed. Withdrawals are subject to a user resources, which means the total amount that user has on account. Another restriction is that a withdrawal amount may not be greater than the value of the till local stock. Tills may keep illegal cards, i.e. after three failed tests for the PIN.
Source: The case has been developed based on the paper: T. Denvir, J. Oliveira, and N. Plat., The Cash-Point (ATM) ’Problem’, Formal Aspects of Computing, 12(4):211–215, 2000, and the ATM use case presented in UML – A Programmers Guide.
Model
BPMN Diagram types:
Process,
Source files: cashpoint.sgx, cashpoint.bpmn
cashpoint-all.pdf
Diagram files: , cashpoint.pdf
Model logic
XTT2 logic model: cashpoint_xtt.hml
Model metrics
Main diagram:
| Abbreviation | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|
| CNC | Coefficient of Network Complexity | 1.33 |
| IC | Interface Complexity Metric | 28.0 |
| NOA | Number of Activities in a Process Metric | 7.0 |
| NOAC | Number of Activities and Control Flow Elements in a Process Metric | 13.0 |
| NOAJS | Number of Activities, Joins and Splits in a Process Metric | 9.0 |
| DSM | Durfee Square Metric | 2.0 |
| PSM | Perfect Square Metric | 4.0 |
| ALL | All Elements | 26.0 |
Authorize client:
| Abbreviation | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|
| CNC | Coefficient of Network Complexity | 0.5 |
| IC | Interface Complexity Metric | 0.0 |
| NOA | Number of Activities in a Process Metric | 2.0 |
| NOAC | Number of Activities and Control Flow Elements in a Process Metric | 2.0 |
| NOAJS | Number of Activities, Joins and Splits in a Process Metric | 2.0 |
| DSM | Durfee Square Metric | 1.0 |
| PSM | Perfect Square Metric | 1.0 |
| ALL | All Elements | 3.0 |